Anti-Aging
Photoaging is a process of aging of the skin attributed to continuous, long-term exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
Collagen is found in the lower part of the dermis and its main function is to give elasticity and hold the skin together. Under the influence of the sun the collagen network breakdown which leads to wrinkle formation and sagging skin. Not only that, but UV also causes increased hyperpigmentation and uneven skin tone.
Ultraviolet light is invisible to humans because it has shorter wavelengths than the light we can see. Within the UV spectrum, we have three main types of UV rays. UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths.
Both UVA and UVB will damage the DNA in the skin cells and even lead to skin cancer. Only UVC cannot reach the earth. It’s important to look for the words “broad spectrum” on a product’s label, which means it has ingredients that can protect you from UVA as well as UVB rays.
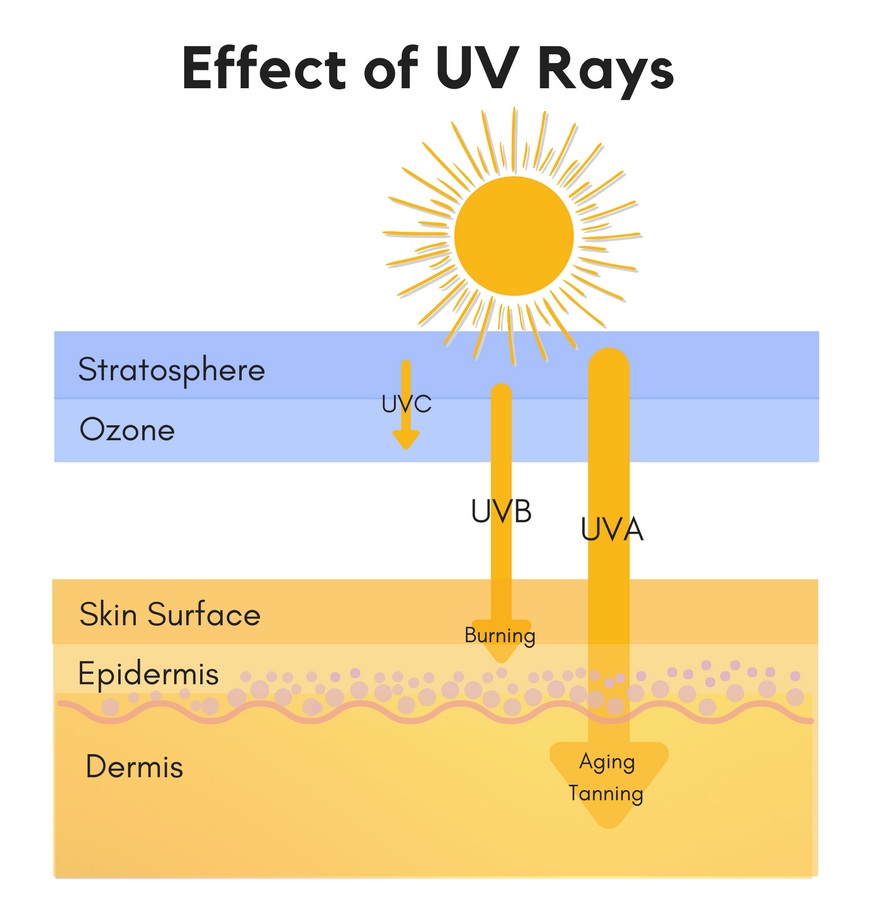
• UVA rays have a longer wavelength that can penetrate the middle layer of your skin (the dermis)
• UVA accounts for about 95% of the UV light that reaches our skin.
• UVA rays from the sun can penetrate through windows and clouds, so wearing a topical antioxidant and sunscreen every day can help protect the skin from the cumulative effects of regular sun exposure,
• UVA rays are reaching into the skin deeper than UVB rays. UVA can deep into the dermis to accelerate collagen breakdown which results in the loss of elasticity, and firmness, cause of wrinkles, uneven skin tone, and dark spots. It plays a part in causing cancer too.
• UVA rays penetrate glass, while UVB rays do not.
• You do not feel the effects of UVA rays damaging your skin, no pain.
• UVB rays have a short wavelength that reaches the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis)
• UVB radiation is powerful: it’s directly responsible for sunburn, redness and sore skin.
• UVB radiation also plays a role in skin cancers
• The SPF number labeled on sunscreen is for UVB protection.
• UVC radiation is the highest energy portion of the UV radiation spectrum. UVC radiation from the sun does not reach the earth’s surface because it is blocked by the ozone layer in the atmosphere. Normally, humans will not be damaged by UVC except through laser and lamp.
| Sunscreen | Mineral/Physical Type | Chemical/Synthetic Type |
|---|---|---|
| Main ingredients | Titanium dioxide and zinc oxide | Oxybenzone, Octinoxate, Octisalate, and Avobenzone |
| How does it works | Work by creating a physical barrier on the skin that shields it from the sun’s rays. | Absorb UV rays before your skin can soak them up |
| Texture | Thicker textures, may leave a white cast | Thinner textures. easier to apply and wear |
| Absorption | Only stay at skin surface | Absorb into the top layers of skin |
| Sensitivity | No risk of irritating skin | Particularly cautious to skin sensitive person |
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor.
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) rating measures how much UVB protection a product provides to the skin. SPF has no relation to UVA protection.
SPF15 means it takes 15 times more solar energy to produce a sunburn compared to unprotected skin. SPF is a measure of how much solar energy (UV radiation) is required to produce sunburn on protected skin (i.e., skin that sunscreen has been applied to) relative to the amount of solar energy required to produce sunburn on unprotected skin. As SPF value increases, sunburn protection increases.
Reapply in every 2 hours when you are outside or immediately after swimming or sweating. We should consider other factors such as the location, altitude and intensity of the sun.
Natural Oil with SPF
Raspberry Seed Oil (SPF 28-60)
Carrot Seed Oil (SPF 18)
Calendula Oil (SPF 15)
Wheatgerm Oil (SPF 22)
Olive and Coconut Oil (SPF 8)
Jojoba Oil
Pomegranate Seed Oil
Shea Butter
Soothing Oil for after sun
Sweet Almond Oil
Avocado Oil
Lavender Oil
Vitamin E Oil
Jojoba Oil
Most people will struggle to use Mineral (Physical) or Synthetic (Chemical) sunscreens, but indeed both of them are effective and have sun protection benefits, which one better is depends on your skin type, preferences, concerns and how sensitive is your skin. For the safe side, I prefer sunscreen with a gentler formulation and the ingredients will not penetrate into the skin.
Limiting your time in the sun, especially between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m., when the sun’s rays are most intense.
Wearing clothing to cover skin exposed to the sun—such as long-sleeve shirts, pants, sunglasses, and broad-brim hats.
Using broad spectrum sunscreens with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) value of 15 or higher regularly and as directed
Wrinkles
Hyperpigmentation (uneven skin tone, dark spots)
Dull Skin
Sunburn
Redness
Dryness and Flaking
Spider Veins
Saggy Skin